Boron trifluoride (BF₃) is an inorganic compound known for its pungent, colorless, and toxic nature. It forms white fumes in the presence of moist air and serves as a versatile Lewis acid, widely utilized as a building block for synthesizing other boron compounds.
The BF₃ molecule has a trigonal planar geometry with D3h symmetry, as predicted by VSEPR theory. Its high symmetry results in no dipole moment. This molecule is often described as "electron-deficient" due to its reactivity with Lewis bases. The B-F bonds are notably shorter than expected for single bonds, possibly indicating π-bonding or an ionic character.
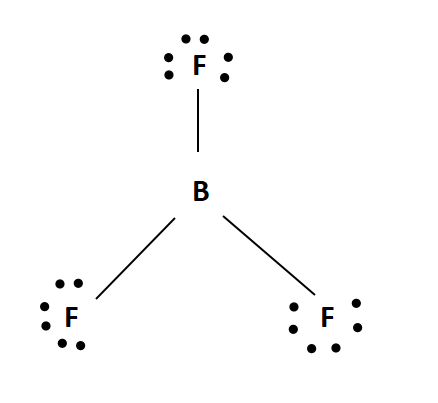
BF₃ is industrially produced by reacting boron oxides with hydrogen fluoride, yielding significant annual production. In laboratory settings, it is often derived from boron trifluoride etherate or via the decomposition of diazonium salts. Handling requires careful consideration, as BF₃ is corrosive and reacts with many materials in the presence of moisture.
BF₃ has a boiling point of −100.3 °C and can only be stored as a refrigerated liquid within specific temperature ranges. It reacts readily with water, forming boric acid and fluoroboric acid, and is used extensively as a Lewis acid in organic chemistry for polymerization, isomerization, and other catalytic processes.
Beyond its chemical reactivity, BF₃ has niche uses in areas such as neutron detection, ion implantation, and as a flux for soldering magnesium. It also plays a role in the preparation of specialized compounds like diborane.
First discovered in 1808, BF₃ continues to be an essential compound in both industrial and scientific domains.
References
Greenwood, N. N., & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier.
Cotton, F. A., Wilkinson, G., Murillo, C. A., & Bochmann, M. (1999). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for Boron trifluoride. Accessed via chemical manufacturers and safety guideline repositories.
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
https://webbook.nist.gov